Mercado Libre = Amazon E-Commerce + Paypal (Deep Dive Act I)
$MELI's Network Effects: Scaling to Continental Dominance
Edited by Brian Birnbaum
Before analyzing Mercado Libre, I reflected on why I hold no ecommerce investments, thus aiming to clarify why Mercado Libre ($MELI) might warrant a place in my portfolio. I found value in this exercise earlier this year, when I exited a small position in Sea Limited ($SE). I realized upon deeper thought that, despite recent positive share price momentum, I lack confidence in the durability of its competitive moat. I came to this realization by articulating my investment criteria and rationale, outlined below:
A Robust Moat: Assures me that a company can thrive regardless of market challenges, maintaining its edge over competitors.
Capable Management with Skin in the Game: Instills confidence that the Moat will endure long-term, with leaders whose interests align with shareholders.
An Asymmetric Bet: Ensures my concentrated portfolio delivers high returns—meaning, while the dogs could lose, say, 50% of their value, the winners should return many times their cost basis, equating to exponential overall portfolio gains.
The content of this analysis is for entertainment and informational purposes only and should not be considered financial or investment advice. Please conduct your own thorough research and due diligence before making any investment decisions and consult with a professional if needed.
Identifying an e-commerce company that meets my portfolio’s criteria for high-growth, sustainable competitive advantages, and asymmetric returns is challenging. In major markets, competition is intense, with no single player guaranteed to dominate long-term due to deep-pocketed rivals and aggressive pricing strategies. In Southeast Asia, while some companies show strong growth, their competitive moats remain unproven, as rivals can replicate logistics networks or outspend on infrastructure, casting doubt on long-term profitability. In mature markets like the U.S. and Europe, dominant players boast robust logistics and customer loyalty but operate in slower-growing environments, with limited contributions from high-growth emerging regions. These dynamics make it difficult to find an e-commerce investment that aligns with my focus on outsized returns in dynamic markets.
Why Mercado Libre Stands Out: MercadoLibre appears to align with my criteria, offering a compelling case for investment:
Undisputed Regional Leader: Mercado Libre commands between 21% and 35% share (according to different sources) of Latin America’s e-commerce market as of 2024, with even stronger dominance in key markets like Brazil, far ahead of its main competitors. This leadership in a high-potential region sets it apart.
Founder-Led with Aligned Management: Founded and led by Marcos Galperin since 1999, MercadoLibre benefits from his strategic vision. Galperin owns 7% of the company, tying his wealth to its success. Long-serving executives promoted internally like Daniel Rabinovich (COO), who joined Mercado Libre in March 2000 as an application architect, and Osvaldo Gimenez (fintech president), who joined Mercado Libre in January 2000 as country manager for Argentina and Chile, demonstrate loyalty and alignment.
Asymmetric Opportunity: Latin America’s e-commerce penetration is low (average across countries 12%), with significant growth potential fueled by rising internet access and favorable demographics. Mercado Libre’s integrated ecosystem—ecommerce, Mercado Pago, and MercadoEnvios (logistics)— likely creates a strong Moat. Diversified revenue streams mitigate risks, such as currency volatility or regulation, while capturing untapped markets like the unbanked. With Latin America’s digital economy projected to explode, Mercado Libre may offer substantial upside with limited downside, considering that current ecommerce penetration is a low-teens percentage of total retail in Latin America, lagging the USA by almost a decade. Third-party forecasts point to the market growing by 54% from $151bn in 2023 to $232bn by 2028.
Given these compelling attributes, Mercado Libre warrants a more thorough analysis to determine its suitability for my highly concentrated portfolio, which currently holds nine stocks.
Index
Mercado Libre at a glance
Mercado Envios, the backbone of MELI’s moat
Mercado Libre ecosystem fosters network effect
Deep Dive Act II
1. Mercado libre at a glance
Mercado Libre’s business operates as an ecosystem of interconnected segments, each addressing specific needs in Latin America’s digital economy. These segments—ecommerce, fintech (Mercado Pago), logistics (Mercado Envios), and additional ventures like advertising and MercadoShops—work together to create a robust platform that drives user engagement and revenue diversification. Below, I detail each segment and the key geographic markets where Mercado Libre operates, focusing on their roles and regional dynamics.
E-commerce (Marketplace)
The core of Mercado Libre’s business is its online marketplace, a platform connecting millions of buyers and sellers. It offers a vast range of products, from electronics to household goods, competing with global giants like Amazon and local retailers. The marketplace thrives on high transaction volumes, earning revenue through commissions, listing fees, and premium seller services. Its strength lies in catering to Latin America’s fragmented retail landscape, where small businesses and informal sellers rely on the platform to reach customers. The segment also includes Mercado Libre’s first-party sales (1P), where it sells directly to consumers, though this is smaller than its third-party marketplace (3P).Fintech (Mercado Pago)
Mercado Pago is Mercado Libre’s payment and financial services arm, a standout growth driver. Initially built to facilitate secure marketplace transactions, it has evolved into a full-fledged fintech platform, offering digital wallets, peer-to-peer payments, QR code-based transactions, and credit products like Mercado Crédito. It serves both online and offline merchants, capturing the region’s underbanked population—over 50% of Latin Americans lack traditional banking access. In 2024, Mercado Pago processed 11 billion transactions, reflecting its scale. It competes with local fintechs like Nubank and global players like PayPal, but its integration with the marketplace provides a unique edge, driving user retention and cross-segment revenue.Logistics (Mercado Envios)
Mercado Envios handles shipping and fulfillment, addressing Latin America’s logistical challenges, such as unreliable postal services and sprawling urban-rural divides. It offers end-to-end solutions, from warehousing to last-mile delivery, enabling faster and more reliable service for marketplace users. Mercado Libre has invested heavily in proprietary logistics networks, including distribution centers and delivery fleets, to reduce dependence on third-party providers. This segment enhances customer experience, boosts seller efficiency, and supports the marketplace’s growth by ensuring timely deliveries in a region where infrastructure is often a bottleneck.Advertising and Mercado Shops
Mercado Libre’s advertising business leverages its massive user base to offer targeted ads, such as sponsored listings and banner placements, to sellers and brands. This high-margin segment capitalizes on the platform’s traffic, competing with digital ad giants like Google and Amazon. Mercado Shops, meanwhile, is a SaaS-like solution that lets businesses create branded online stores hosted by Mercado Libre and integrated with its payment and logistics services. While smaller than other segments, both advertising and Mercado Shops contribute to revenue diversification and strengthen the ecosystem’s stickiness.
Mercado Libre operates across 18 countries in Latin America, with varying degrees of penetration and market dynamics. The key markets include:
Brazil: The largest economy in Latin America, Brazil is Mercado Libre’s biggest market by revenue. Its e-commerce sector is growing rapidly, driven by a large population (over 200 million) and increasing smartphone penetration. Mercado Libre faces competition from Amazon, Shopee, and local players like Magazine Luiza, but its logistics and fintech integration maintain its edge. Brazil’s fragmented retail and low banking penetration make it a prime market for both the marketplace and Mercado Pago.
Argentina: Mercado Libre’s home country, Argentina, is a significant market despite economic volatility, including hyperinflation and currency fluctuations. The platform thrives here due to limited competition and high demand for digital solutions amid economic instability. Mercado Pago is particularly strong, offering a hedge against cash-based transactions in a crisis-prone economy.
Mexico: Mexico’s proximity to the U.S. and growing middle class make it a key growth market. Ecommerce adoption is accelerating, but competition is fierce from Amazon, Walmart, and local players like Liverpool. Mercado Libre’s localized approach, including tailored logistics and payment solutions, helps it capture share in this densely populated market of 130 million.
Other Markets: Countries like Chile, Colombia, and Peru are smaller but fast-growing, with rising internet access fueling e-commerce demand. These markets have less competition from global players, allowing Mercado Libre to establish early dominance. For example, in Colombia, Mercado Libre is a go-to platform for urban consumers, while in Chile, it benefits from a stable economy conducive to digital adoption.
2. Mercado Envios, the backbone of MELI’s moat
Mercado Libre began developing its logistics arm, Mercado Envios, in 2013. This initiative was launched to address the significant logistical challenges in Latin America, such as unreliable delivery systems and underdeveloped infrastructure, which were hindering ecommerce growth. Initially, Mercado Envios integrated with third-party logistics providers, but the company quickly shifted to building its own network, Meli Net, incorporating cross-docking, warehousing, fulfillment, and last-mile delivery operations to enhance scalability and customer experience. By 2020, 62% of marketplace items (406 million) were shipped via Mercado Envios, more than quadrupling the 102 million items from 2019, showcasing its rapid development.
Mercado Libre is not only capturing the lion’s share of Latin America’s ecommerce market growth but is also likely driving the market’s expansion through unmatched efficiency in a fragmented landscape. A clear sign is Mercado Libre’s Gross Merchandise Value (GMV), which is growing at a faster rate than the region’s ecommerce GMV ex-Mercado Libre, underscoring its role in both seizing and stimulating market demand.
In 2024, the company processed 1.8 billion items through a network of over 90 logistics centers, bolstered by strong new investments in new fulfillment centers and other logistic infrastructure. This represents a 2.7X increase since 2020 alone.
In Q3, we opened six new fulfillment centers, five in Brazil and one in Mexico, and that helps us improve or increase fulfillment penetration by 4.5 percentage points compared to a year ago. We know that having more volume shipped out of our own fulfillment facilities results in a much better user experience for buyers and sellers in faster and more reliable delivery speeds and a much better conversions of volume, in turn, results in further growth of the ecosystem,
explained during the Q3 2024 earnings call Marcos Galperin, CEO of the Company.
We are not only building warehouses in the main capitals of the countries as we have announced. We are also regionalizing our capacity more and that means that we'll be better equipped to serve our customers with faster delivery promises and hence, better [hopefully] retention rates coming from them,
said Commerce President Ariel Szarfsztejn, going deeper during the Q2 2024 earnings call.
Meli’s infrastructure enabled 49% of Q4 shipments to reach customers same-or next-day—up 21% year-over-year—with over 95% handled in-house, a metric CEO Marcos Galperin hailed as “a game-changer for trust and reliability” in the Mercado Libre Q4 2024 Earnings Call.
Amazon operates approximately 45-50 logistics facilities across Latin America as of 2024—around 40 in Mexico and 5-10 in Brazil—and faces slower delivery times (pretty decent across all Mexico, 1-2 days in select cities like Mexico City and São Paulo, but significantly longer elsewhere in the region). In contrast, Mercado Libre’s customized logistics network minimizes per-package costs and capitalizes on regional efficiencies, such as cross-border inventory sharing, to surpass competitors.
Our logistics isn’t just about speed; it’s about owning the customer experience end-to-end,
CEO Marcos Galperin highlighted during the Q3 2024 earnings call.
Mercado Libre’s logistics efficiency drove a $14.5 billion GMV in Q4 2024, with Mexico and Brazil achieving 28% and 32% FX-neutral growth rate, respectively, cementing its regional dominance.
In 2024, Mercado Libre’s managed logistics network handled 95% of shipped items, a significant leap from 63% in 2020, with 72% delivered within 48 hours, demonstrating increasing user trust in its advanced infrastructure.
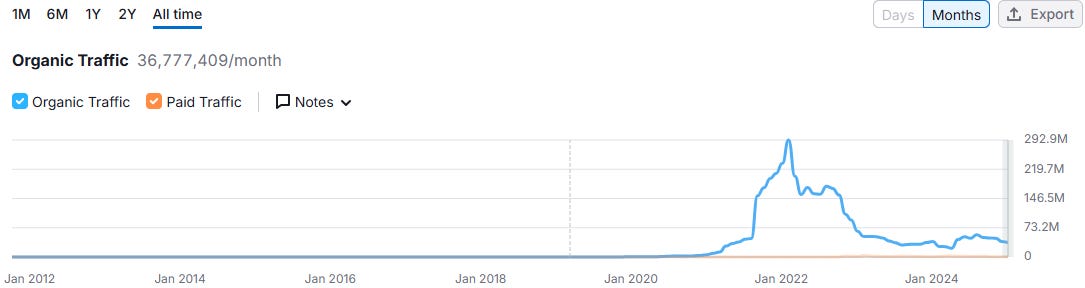
To further confirm Mercado Libre’s regional leadership, let’s compare the website traffic of its local platforms with those of its primary competitors, Amazon and Shopee, in their strongest markets, assuming Mercado Libre’s dominance is even more pronounced across other Latin American markets.
In Brazil, Mercado Libre's website leads with roughly twice the organic traffic of Amazon and 4.2 times the organic traffic of Shopee.
In Mexico, Mercado Libre's website leads with twice the organic traffic of Amazon and 141X the organic traffic of Shopee.
Having established Mercado Libre as the unrivaled leader in Latin America’s ecommerce market, with Mercado Envios serving as a key pillar of its competitive moat, it’s reasonable to infer that sustained investment in logistics infrastructure will likely preserve its dominance, particularly in markets where competitors like Amazon and Shopee lag in logistics development. While Amazon and Shopee may slowly narrow the gap in Brazil and Mexico, Mercado Libre’s edge is likely to endure in other countries with less competitor investment, such as Argentina.
Although precise data on Amazon and Shopee’s logistics investments in Latin America is unavailable due to their broader global operations, a useful proxy is to compare the “Net Property, Plant, and Equipment” (PP&E) trends from the balance sheets of Mercado Libre and Sea Limited. Such value indicates the Gross Property Plant & Equipment stated at cost minus Accumulated Depreciation. While absolute values are not comparable due to their distinct geographic scopes, the trends are revealing.
Sea Limited’s PP&E peaked in 2022 and has since declined, suggesting a shift from expansion to optimizing profitability in existing markets. In contrast, Mercado Libre’s PP&E has grown steadily, surpassing Sea’s in absolute terms by 2024. This trajectory mirrors Amazon’s playbook, indicating that Mercado Libre is aggressively expanding its physical infrastructure—much like Amazon has in the U.S. and Europe—positioning it to secure and maintain market leadership in Latin America for the foreseeable future.
To further demonstrate Mercado Libre’s operational efficiency and the tangible scale economies derived from its logistics infrastructure, I analyzed the Cash Flow from Operations (CFO) to PP&E ratio for MELI and Sea. Although the two companies operate in different regions—Sea primarily in Asia-Pacific and MELI exclusively in Latin America—their revenue scales are comparable, with MELI surpassing Sea’s revenue in 2024. Both companies also share similar business models, with Sea operating a fintech arm alongside its e-commerce platform, much like MELI. Given Sea’s decreasing PP&E in 2023 and 2024 (which lowers the denominator), one might expect Sea’s ratio to rise sharply and potentially outperform MELI in absolute terms, especially since Sea’s gaming business (which adds to the e-commerce and fintech businesses) should generate additional cash with a lower fixed cost structure. However, the data paints a different picture.
While Sea’s ratio indeed grew in 2023 and 2024, MELI’s ratio not only remains higher in absolute terms but has also been steadily increasing since 2021, confirming the presence of robust scale economies with no signs of slowing. This KPI comparison, combined with MELI’s continued CAPEX growth contrasted against Sea’s slowdown in capital investments, provides a strong indication of the divergent trajectories of the two businesses, with MELI maintaining a stronger upward momentum.
3. Mercado Libre ecosystem fosters network effect
As CEO Marcos Galperin noted (Mercado Libre Q4 2023 Earnings call),
Each new user makes our ecosystem more valuable for everyone
Unlike competitors like Shopee, which rely on third-party logistics, Mercado Libre’s integrated network effect across its marketplace, payments, and logistics creates a sticky, scalable platform that solidifies its regional leadership.
Complementing the e-commerce platform, Mercado Pago offers a versatile suite of financial services, including digital payments, credit solutions, and merchant tools, fostering financial inclusion and streamlining transactions.
The integration of these platforms creates a virtuous cycle: ecommerce fuels payment adoption, while fintech enhances user trust and merchant efficiency, solidifying MELI’s position as Latin America’s digital commerce leader.
The integration of Mercado Libre’s ecommerce and Mercado Pago fintech platforms creates powerful network effects.
As more consumers shop on the e-commerce platform—100m annual unique buyers in 2024, up 17.6% from 2023— Mercado Pago’s payment and credit services gain users.
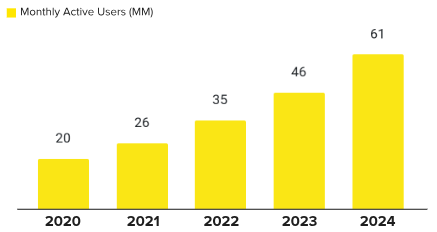
In 2024, Mercado Pago reported 61 million monthly active users, a 32.6% increase from 2023, and a transaction volume of $11.3 billion, up 49.5% year-over-year. This rapid growth highlights Mercado Pago’s non-linear benefits from its integration with MercadoLibre, as the fintech platform scales exponentially with rising user numbers and increased engagement.
Rising user growth draws more merchants, who capitalize on a larger buyer base and benefit from efficient payment systems and financing options, enhancing the platform’s offerings. A broader merchant network attracts even more buyers, boosting traffic and transactions, and reinforcing MercadoLibre’s dominance in Latin America’s digital ecosystem.
MercadoLibre’s network effect is vividly demonstrated by several metrics. Let’s zoom in on those most relevant.
The following chart underscores MercadoLibre’s network effect by showcasing rising user engagement and purchase frequency from 2019 to 2024, as buyers increasingly interact with the platform across more categories. The left graph reveals a 432% increase in buyers purchasing from three or more categories, growing steadily from 2019 to 2024, indicating deeper user engagement as the platform’s diverse offerings attract and retain users. The right graph complements this, showing average quarterly items purchased per buyer rising from 4.4 in 2019 to 7.5 in 2024, a 71% increase, reflecting higher purchase frequency. As more buyers engage across categories, merchants are incentivized to join and expand their offerings, further enriching the platform.
Mercado Pago’s functionality extends beyond Mercado Libre’s core ecosystem, catering to non-ecosystem users for payments and financial services, which is particularly noteworthy when analyzing the comparative performance of ecosystem users—those engaging with both the e-commerce platform and Mercado Pago—versus users solely utilizing Mercado Pago.
On the left, the Monthly Payment Volume (TPV), on the right, the Non-Performing Loans.
Ecosystem users exhibit significantly higher engagement, with a Monthly TPV Index of 118 for debit card users and 144 for credit card users, compared to 100 for non-ecosystem users, reflecting increased transaction frequency driven by the integrated experience. Additionally, ecosystem users pose lower credit risk, with a “Credit Card NPL (Non Performing Loan) >30 Days” Index of 51 versus 100 for non-ecosystem users, indicating greater reliability that attracts merchants and lenders to the platform.
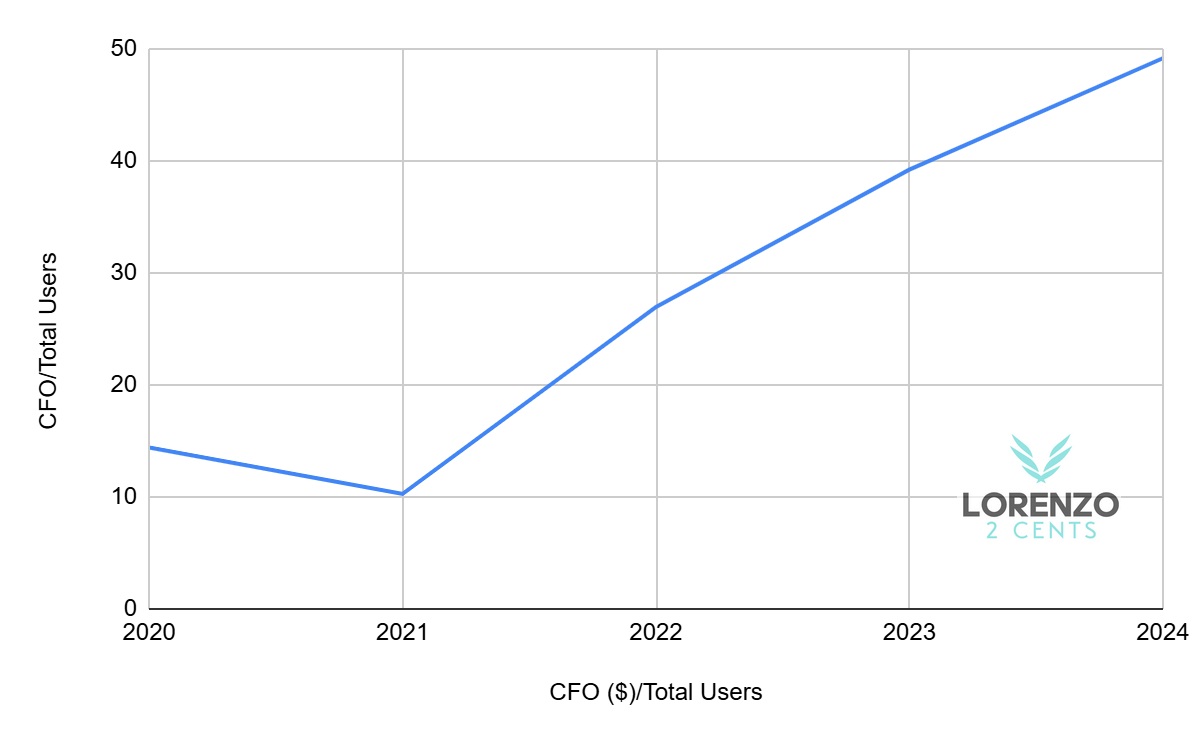
Mercado Libre’s network effect across its entire ecosystem is also powerfully reflected in the Cash Flow from Operations (CFO) per Total Active Users metric, which quantifies the cash generated per user within its integrated e-commerce and fintech platforms. CFO serves as a critical indicator of network effects, capturing the financial impact of heightened user and merchant interactions throughout the ecosystem: a growing user base drives higher transaction volumes, fuels additional commerce services like advertising revenue, and indirectly boosts acquiring revenue by encouraging more merchants to adopt Mercado Pago’s off-platform services, ultimately enhancing operational cash flows as the ecosystem scales—evidenced by MELI’s 54% Free Cash Flow (FCF) growth in 2024. In 2024, with an estimated CFO of $7.9 billion and 161 million total active users (100 million unique buyers plus 61 million Mercado Pago MAUs, without deduplication), MELI generated approximately $49 per user, as depicted in the accompanying chart tracking this metric from 2020 to 2024.
Despite its conservative bias—stemming from overlapping e-commerce and fintech users inflating the denominator (lack of deduplication)—the metric’s consistent rise from $14 in 2020 to $49 in 2024 highlights MELI’s increasing operational efficiency. This upward trajectory demonstrates how network effects amplify cash flows, with a larger user base driving more transactions and merchant engagement, solidifying MELI’s ecosystem strength and reinforcing its leadership in Latin America’s digital economy.
MercadoLibre’s penetration of the Latin American economy is so profound that we could speculate its network effects extend to a continental scale, creating a self-reinforcing cycle that amplifies its impact far beyond traditional metrics. Operating across 18 countries with localized platforms, MELI has become deeply embedded in the region’s economic fabric, commanding unparalleled organic traffic. This extensive reach reduces economic frictions such as limited access to goods, high transaction costs, and financial exclusion. As MELI penetrates deeper into the market these frictions will diminish further, enabling greater consumer spending and accelerating adoption of its ecosystem. For instance, the platform’s logistics arm, Mercado Envíos, facilitates seamless delivery, while Mercado Pago’s credit portfolio empowers users to spend more, driving transaction volumes and attracting more merchants. This continent-level network effect creates a virtuous cycle: increased adoption lowers barriers, fuels economic activity, and solidifies MELI’s ecosystem as the backbone of Latin America’s digital economy, positioning it as an unrivaled leader in the region.
4. Deep Dive Act II
In the second installment of this deep dive, I will compare Mercado Pago and Nubank to determine which company is driving the fintech agenda in Latin America. As always, I will construct a Business Ontology for Mercado Libre to track its performance over time, evaluate whether the common Bear Case Thesis holds up, and share whether I ultimately invested in the company after dissecting its business in this analysis.
Subscribe and Stay Tuned For MELI Deep Dive Act II!
In the meantime, explore my other deep dives on HIMS 0.00%↑ , DUOL 0.00%↑ , RKLB 0.00%↑ , ODD 0.00%↑ , LMND 0.00%↑ , and CRWD 0.00%↑ .


















We look forward to the comparison between NU bank and Mercado Pago.
Excelente Lorenzo!!!!!